CAN FD (flexible data rate) - The basic idea
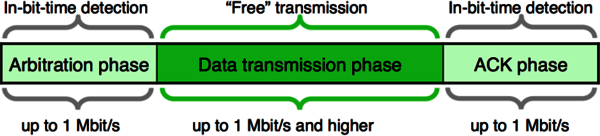
Because of the bandwidth requirements of the automotive industry, the CAN data link layer protocol needed to be improved. In 2011, Robert Bosch GmbH started the CAN FD (flexible data rate) development in close cooperation with carmakers and other CAN experts. The improved protocol overcomes two CAN CC (classic) limits: You can transmit data faster than with 1 Mbit/s and the payload (data field) is now up to 64 byte long and not limited to 8 byte anymore. In general, the idea is simple: When just one node is transmitting, the bit rate can be increased, because no nodes need to be synchronized. Of course, before the transmission of the ACK slot bit, the nodes need to be re-synchronized.
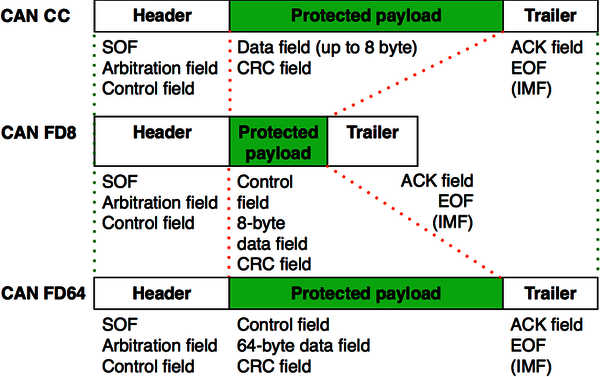
Using a ratio of 1:8 for the bit rates in the arbitration and data phase leads to an approximately six times higher throughput considering that the CAN FD frames use more bits in the header (control field) and in the CRC field.
CAN FD – Some protocol details
In order to distinguish between CAN CC data frames and CAN FD data frames, one of the formerly reserved bits is used. This bit is called FD frame (FDF) bit. If it is of recessive value, the following bit sequence is interpreted as a CAN FD data frame. If it is of dominant value, it is a CAN CC data or remote frame. In the newly introduced bit rate switch (BRS) bit, the second bit rate is applied, when it is of recessive (r) value. If it is of dominant (d) value, the arbitration phase bit time setting is used in the data phase, too.
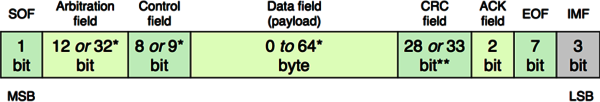
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| SOF | start of frame |
| CRC | cyclic redundancy check |
| ACK | acknowledgement |
| EOF | end of frame |
| IMF | intermission field |
The CAN FD protocol controller also supports CAN CC frames. CAN CC as well as CAN FD are internationally standardized together in ISO 11898-1:2024. CAN FD data frames with 11-bit identifiers use the FD base frame format (FBFF) and those with 29-bit identifiers use the FD extended frame format (FEFF). The CAN FD protocol does not support remotely requested data frames.
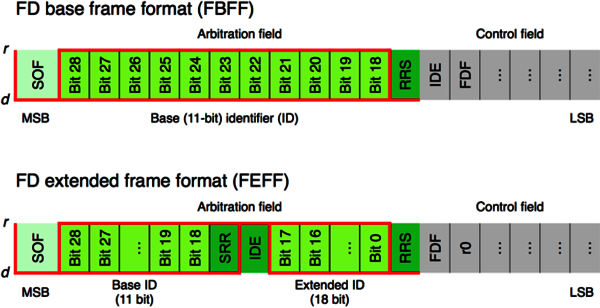
| Field | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| RRS | remote request substitution | |
| SRR | substitute remote request | |
| IDE | identifier extension | |
| FDF | flexible data rate format | |
| d | dominant | |
| r | recessive | |
| r0 | reserved |
The control field comprises additional bits not provided by the CAN CC data frames. The FDF bit indicates the usage of FD frame formats. At the sample-point of the BRS bit, the bit rate switch is performed. This guarantees a maximum of robustness. The following error state indicator (ESI) bit provides information about the error status: a dominant value indicates an error active state.
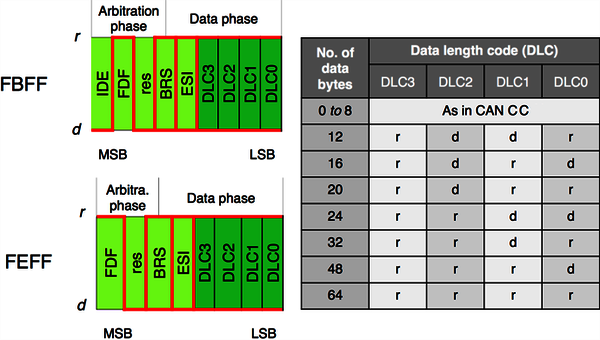
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| IDE | identifier extension |
| FDF | flexible data rate format |
| BRS | bit rate switch — recessive, if alternate bit rate |
| ESI | error state indicator — recessive, if error passive |
| DLC | data length code |
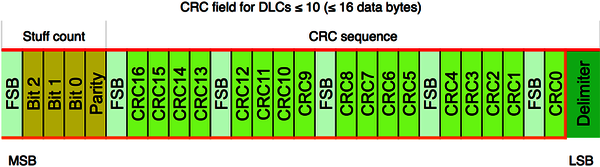
During the standardization process of the CAN FD protocol, some additional safe guards were introduced in order to improve the communication reliability. This is why the CRC field comprises 17-bit (for frames with payloads up to 16 byte) or 21-bit (for frames larger than 16 byte) polynomials and an 8-bit stuff-bit counter plus a parity bit. The CRC field use fixed stuff-bits (FSB) with an opposite value of the previous bit. All these safe guards guarantee that all single failures are detected under all conditions. Even the possibility to detect multiple failures has been improved.
Medium-term, non-ISO CAN FD controllers might also be on the market – these are not compliant with the ISO 11898-1. They don’t implement the above-mentioned additional safe guard features.
| Title | Details | Published Size |
Status Action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
ScopeThis set of documents specifies and recommends the usage of CAN FD hardware implementations. It consists of the following parts: Part 1: Physical interface implementation, Part 2: Controller interface specification, Part 3: System design recommendation, Part 4: Ringing suppression. This part provides specifications and guidelines on the physical layer interface design for automotive electronic control units and non-automotive devices supporting the CAN FD data link layer as defined in ISO 11898-1 and the CAN high-speed physical layer as defined in the harmonized ISO 11898-2 standard, which includes the specification of high-speed transceivers with low-power mode (formerly known as ISO 11898-5) and/or with selective wake-up functionality (formerly known as ISO 11898-6). |
2021-03-08 818 KB | TR Login |
|
|
ScopeThis set of documents specifies and recommends the usage of CAN FD hardware implementations. It consists of the following parts: Part 1: Physical interface implementation, Part 2: Controller interface specification, Part 3: System design recommendation, Part 4: Signal improvement, Part 6: CAN FD cable. This part specifies the requirements and test methods of the mechanical and electrical parameters for cables to be used in CAN FD networks. |
2019-09-06 227 KB | DS Login |
|
|
ScopeThis document specifies additional requirements for CAN transceivers compliant with ISO 11898-2:2016 for the purpose to reduce differential and common-mode ringing on the CAN_H and CAN_L wires, namely the CAN SIC transceiver. Furthermore, this document specifies EMC tests for the CAN SIC transceiver. |
2023-09-01 77 KB | withdrawn Login |
|
|
ScopeThis set of documents recommends the usage of CAN FD hardware implementations. It consist of the following parts: Part 1: Physical interface implementation, Part 2: CAN controller interface specification, Part 3: System design recommendation, Part 4: Signal improvement. This part provides recommendations for CAN FD network design, especially, bit-timing setting rules and guidelines are given. This part also includes the spreadsheet that helps to perform the CAN clock tolerance calculation, the bit-timing evaluation and optimization, the bit asymmetries calculation, and the evaluation of the robustness. |
2021-03-08 682 KB | TR Login |
|
|
ScopeThis set of documents specifies and recommends the usage of CAN FD hardware implementations. It consists of the following parts: Part 1: Physical interface implementation, Part 2: Controller interface specification, Part 3: System design recommendation, Part 4: Ringing suppression. This part describes the specified interface between the protocol controller implementing the CAN FD data link layer protocol and the host controller including necessary configuration registers. Such a harmonized interface reduces the effort for adapting the low-level driver software to different implementations. |
2025-05-06 83 KB | withdrawn Login |
|
|
Scope |
2025-07-24 412 KB | WD Login |
|
|
Scope |
2025-08-20 1 MB | WD Login |
|
|
Scope |
2025-08-20 957 KB | WD Login |
|
|
Scope |
2015-10-30 264 KB | WD Login |
|
|
ScopeThis document specifies the time-stamping, when transmitting and receiving CAN data frames in classical CAN and CAN FD formats. This time synchronization can be used in particular in AUTOSAR environments. Therefore, a link to the AUTOSAR time synchronization is described. |
2023-09-01 458 KB | DS Login |